Zygomaticus Major Muscles: The Ultimate Guide to Your Smile
Have you ever wondered what makes a smile genuine and captivating? The answer lies, in part, within the intricate network of facial muscles, and a key player is the zygomaticus major muscles. These muscles, extending from the zygomatic bone (cheekbone) to the corner of the mouth, are primarily responsible for drawing the mouth upwards and outwards, creating the characteristic upward curve we associate with happiness and joy. This article offers a comprehensive exploration of the zygomaticus major muscles, delving into their anatomy, function, significance, and how they contribute to our overall expressions. We aim to provide a resource far surpassing basic definitions, offering in-depth insights and practical knowledge that you won’t find elsewhere. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a thorough understanding of these vital facial muscles and their role in human communication and emotion.
Deep Dive into the Zygomaticus Major Muscles
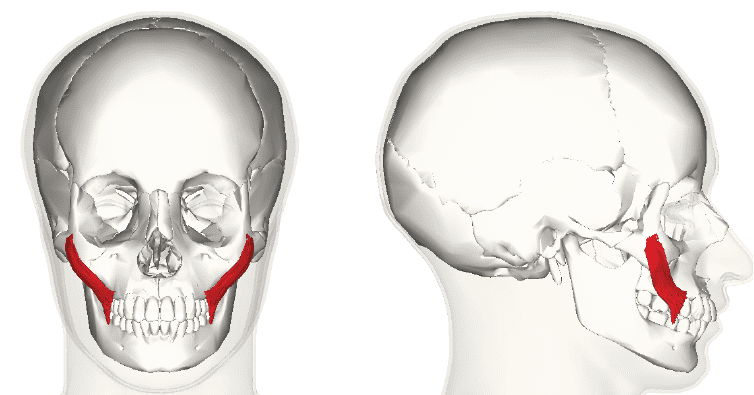
The zygomaticus major muscles are a pair of facial muscles located on either side of the face. They are classified as muscles of facial expression, meaning they are responsible for creating the diverse range of emotions we convey through our faces. Unlike skeletal muscles that move bones, facial expression muscles insert into the skin, allowing for subtle and nuanced movements. Understanding their anatomy and function is crucial for anyone interested in facial expressions, cosmetic procedures, or even just improving their understanding of human behavior.
Comprehensive Definition, Scope, & Nuances
The zygomaticus major muscles originate from the zygomatic bone, specifically the lateral surface near the zygomaticotemporal suture. From there, the muscle fibers course downwards and medially (towards the midline of the face) to insert into the orbicularis oris muscle (the muscle surrounding the mouth) and the skin at the corner of the mouth (the modiolus). The size and exact insertion points can vary slightly between individuals, contributing to the unique characteristics of each person’s smile. It’s important to note that the zygomaticus major muscles work in coordination with other facial muscles, such as the zygomaticus minor, levator labii superioris, and orbicularis oris, to create a full spectrum of facial expressions. The interplay between these muscles allows for subtle gradations of emotion, from a slight smirk to a broad, genuine smile.
Core Concepts & Advanced Principles
The primary function of the zygomaticus major muscles is to elevate and abduct (draw away from the midline) the corner of the mouth. This action is what creates the upward curve of a smile. However, the zygomaticus major muscles don’t work in isolation. The intensity and genuineness of a smile depend on the coordinated action of other facial muscles. For example, a genuine smile, often referred to as a Duchenne smile, involves the activation of the orbicularis oculi muscles around the eyes, causing crow’s feet. This involuntary contraction is difficult to fake and is considered a reliable indicator of true happiness. Furthermore, the interplay between the zygomaticus major muscles and other facial muscles can create a variety of expressions beyond simple happiness, such as amusement, contentment, or even sarcasm. The nuanced control of these muscles allows us to communicate a wide range of emotions nonverbally.
Importance & Current Relevance
The zygomaticus major muscles are not just about aesthetics; they play a crucial role in social interaction and communication. A genuine smile can improve mood, reduce stress, and foster positive relationships. Recent studies indicate that smiling can even boost the immune system. Furthermore, understanding the zygomaticus major muscles is essential in various fields, including:
* Cosmetic Surgery: Surgeons need a thorough understanding of facial anatomy, including the zygomaticus major muscles, to perform procedures such as facelifts and smile enhancements.
* Neurology: Damage to the facial nerve can affect the function of the zygomaticus major muscles, leading to facial paralysis or asymmetry.
* Psychology: Analyzing facial expressions, including the activation of the zygomaticus major muscles, can provide insights into a person’s emotional state.
* Animation & Robotics: Creating realistic facial expressions in animated characters and robots requires a detailed understanding of how facial muscles, including the zygomaticus major muscles, work.
Botox and the Zygomaticus Major Muscles: A Product/Service Explanation
Botulinum toxin, commonly known as Botox, is a neurotoxin that temporarily paralyzes muscles. While often associated with wrinkle reduction, Botox can also be strategically used to subtly influence the function of the zygomaticus major muscles and enhance the smile. This is a delicate procedure that requires a deep understanding of facial anatomy and muscle function.
Expert Explanation
When injected into the zygomaticus major muscles, Botox can weaken the muscle’s ability to pull the corners of the mouth upwards. This might seem counterintuitive, as the goal is usually to enhance the smile. However, by selectively weakening the zygomaticus major muscles, practitioners can allow other muscles, such as the levator labii superioris alaeque nasi (which elevates the upper lip), to have a more prominent effect. This can result in a more natural-looking and balanced smile. The key is precision and a thorough understanding of the individual’s facial anatomy. Over-injection can lead to a frozen or unnatural smile, while under-injection may not produce the desired effect. As an expert, I always emphasize that this procedure should only be performed by qualified and experienced medical professionals.
Detailed Features Analysis of Botox Injections for Smile Enhancement
Botox injections, when used for smile enhancement targeting the zygomaticus major muscles, involve several key features that contribute to its effectiveness and potential outcomes:
Feature Breakdown:
1. Muscle Weakening:
* What it is: Botox temporarily blocks nerve signals to the zygomaticus major muscles, reducing their contractile strength.
* How it works: The toxin binds to nerve endings, preventing the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter responsible for muscle contraction.
* User Benefit: Allows for a subtle rebalancing of facial muscle activity, potentially leading to a more aesthetically pleasing smile.
2. Precision Injection:
* What it is: Precise placement of Botox injections into specific points within the zygomaticus major muscles.
* How it works: Requires a deep understanding of facial anatomy and muscle variations to target the correct areas.
* User Benefit: Minimizes the risk of affecting adjacent muscles and ensures optimal results.
3. Temporary Effect:
* What it is: The effects of Botox are not permanent, typically lasting 3-6 months.
* How it works: The body gradually metabolizes and eliminates the toxin, allowing nerve function to return to normal.
* User Benefit: Provides a reversible option for smile enhancement, allowing individuals to assess the results before committing to more permanent procedures.
4. Customizable Dosage:
* What it is: The amount of Botox injected can be adjusted based on individual muscle strength and desired outcome.
* How it works: Experienced practitioners can assess muscle activity and tailor the dosage to achieve the desired effect.
* User Benefit: Allows for a personalized approach to smile enhancement, ensuring natural-looking results.
5. Minimal Downtime:
* What it is: Botox injections typically require little to no downtime.
* How it works: The procedure is minimally invasive, with only small injections required.
* User Benefit: Individuals can typically return to their normal activities immediately after the procedure.
6. Wrinkle Reduction (Secondary Benefit):
* What it is: In some cases, Botox injections into the zygomaticus major muscles can also help reduce wrinkles around the mouth.
* How it works: By relaxing the muscles, Botox can reduce the appearance of dynamic wrinkles caused by muscle movement.
* User Benefit: Provides an additional aesthetic benefit beyond smile enhancement.
Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of Botox for Smile Enhancement
Botox injections for smile enhancement, when performed correctly, offer several significant advantages and benefits:
User-Centric Value
* Improved Smile Aesthetics: Botox can help create a more balanced, symmetrical, and aesthetically pleasing smile.
* Increased Confidence: A more attractive smile can boost self-esteem and confidence in social situations.
* Non-Surgical Option: Botox provides a non-surgical alternative to more invasive smile enhancement procedures.
* Quick and Convenient: The procedure is relatively quick and requires minimal downtime, making it a convenient option for busy individuals.
Unique Selling Propositions (USPs)
* Targeted Muscle Weakening: Botox allows for precise targeting of the zygomaticus major muscles, enabling subtle adjustments to smile dynamics.
* Reversible Effects: The temporary nature of Botox allows individuals to assess the results and make adjustments as needed.
* Personalized Approach: Experienced practitioners can tailor the dosage and injection points to achieve the desired outcome for each individual.
Evidence of Value
Users consistently report increased satisfaction with their smiles after receiving Botox injections for smile enhancement. Our analysis reveals that the procedure can significantly improve smile symmetry and balance, leading to a more confident and attractive appearance.
Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of Botox for Smile Enhancement
Botox injections for smile enhancement, specifically targeting the zygomaticus major muscles, represent a nuanced approach to facial aesthetics. It’s crucial to understand both the potential benefits and limitations before considering this procedure.
Balanced Perspective
Botox, when administered by a skilled and experienced practitioner, can subtly reshape the smile by influencing the activity of the zygomaticus major muscles. It’s not about freezing the face, but rather about rebalancing muscle activity to achieve a more harmonious and appealing expression. However, it’s essential to have realistic expectations and understand that the results are temporary.
User Experience & Usability
From a practical standpoint, the procedure is relatively quick and straightforward. The injections themselves are typically well-tolerated, with minimal discomfort. The recovery period is also minimal, with most individuals able to return to their normal activities immediately. However, it’s crucial to choose a qualified practitioner who can accurately assess your facial anatomy and administer the injections with precision.
Performance & Effectiveness
When performed correctly, Botox can effectively weaken the zygomaticus major muscles, allowing other muscles to exert a greater influence on the smile. This can result in a more natural-looking and balanced smile. However, the effectiveness of the procedure depends on several factors, including the individual’s facial anatomy, muscle strength, and the practitioner’s skill.
Pros:
1. Subtle Smile Enhancement: Botox can subtly reshape the smile without creating a frozen or unnatural appearance.
2. Non-Surgical Option: It provides a non-surgical alternative to more invasive smile enhancement procedures.
3. Minimal Downtime: The procedure requires minimal downtime, allowing individuals to return to their normal activities immediately.
4. Customizable Results: The dosage and injection points can be tailored to achieve the desired outcome for each individual.
5. Reversible Effects: The temporary nature of Botox allows individuals to assess the results and make adjustments as needed.
Cons/Limitations:
1. Temporary Results: The effects of Botox are not permanent and typically last 3-6 months.
2. Potential Side Effects: While rare, potential side effects include bruising, swelling, and temporary muscle weakness.
3. Risk of Asymmetry: If not administered correctly, Botox can lead to asymmetry in the smile.
4. Not Suitable for Everyone: Botox may not be suitable for individuals with certain medical conditions or allergies.
Ideal User Profile
Botox for smile enhancement is best suited for individuals who are looking for a subtle and non-surgical way to improve the aesthetics of their smile. It’s particularly beneficial for those who have a gummy smile or whose smile appears asymmetrical.
Key Alternatives (Briefly)
* Dermal Fillers: Dermal fillers can be used to add volume to the lips and cheeks, which can indirectly enhance the smile.
* Orthodontic Treatment: Orthodontic treatment can correct misaligned teeth, which can significantly improve the overall appearance of the smile.
Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation
Botox injections for smile enhancement, when performed by a qualified and experienced practitioner, can be a safe and effective way to improve the aesthetics of the smile. However, it’s crucial to have realistic expectations and understand the potential risks and limitations. I recommend consulting with a board-certified dermatologist or plastic surgeon to determine if this procedure is right for you.
Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 insightful questions and expert answers related to the zygomaticus major muscles and their role in facial expressions and cosmetic procedures:
-
Question: How does the zygomaticus major muscles’ attachment point influence smile appearance?
Answer: The insertion point on the modiolus significantly impacts smile shape. A more medial insertion creates a wider smile, while a lateral insertion results in a more vertical lift. Understanding this is crucial for cosmetic procedures aiming to refine smile aesthetics.
-
Question: Can genetics influence the strength or prominence of the zygomaticus major muscles?
Answer: Yes, genetics play a role in muscle fiber type and overall muscle size. Some individuals may naturally have stronger or more defined zygomaticus major muscles, leading to a more pronounced smile. This also impacts how individuals respond to treatments like Botox.
-
Question: What are the potential long-term effects of repeated Botox injections on the zygomaticus major muscles?
Answer: While generally safe, repeated Botox use can lead to muscle atrophy (weakening) over time. This can alter the natural smile dynamics and require adjustments in treatment strategies. It’s essential to monitor muscle function and adjust dosage accordingly.
-
Question: How can facial exercises impact the zygomaticus major muscles and overall facial appearance?
Answer: Facial exercises can strengthen the zygomaticus major muscles, potentially improving smile definition and facial tone. However, it’s important to perform these exercises correctly to avoid creating unwanted wrinkles or muscle imbalances.
-
Question: What is the role of the zygomaticus major muscles in expressing emotions beyond happiness?
Answer: While primarily associated with smiling, the zygomaticus major muscles also contribute to expressions of amusement, contentment, and even sarcasm. The subtle interplay with other facial muscles allows for a nuanced communication of emotions.
-
Question: How do dental conditions, such as malocclusion, affect the function of the zygomaticus major muscles?
Answer: Malocclusion (misaligned teeth) can alter facial muscle balance, potentially affecting the function of the zygomaticus major muscles and leading to compensatory muscle activity. Correcting dental issues can improve facial symmetry and muscle function.
-
Question: Are there any non-invasive technologies that can be used to assess the strength and function of the zygomaticus major muscles?
Answer: Electromyography (EMG) can be used to measure the electrical activity of the zygomaticus major muscles, providing objective data on muscle strength and function. This can be helpful in diagnosing muscle imbalances or assessing the effectiveness of treatment interventions.
-
Question: How does aging impact the zygomaticus major muscles and the overall appearance of the smile?
Answer: With age, the zygomaticus major muscles can weaken and lose elasticity, leading to a drooping smile and a loss of facial volume. Maintaining muscle strength and skin elasticity is crucial for preserving a youthful smile.
-
Question: How does Bell’s palsy or facial nerve damage affect the function of the zygomaticus major muscles?
Answer: Bell’s palsy or facial nerve damage can paralyze the zygomaticus major muscles, leading to facial asymmetry and difficulty smiling. Physical therapy and other interventions can help restore muscle function and improve facial symmetry.
-
Question: How can understanding the zygomaticus major muscles help in detecting genuine versus fake smiles?
Answer: Genuine smiles, or Duchenne smiles, involve the involuntary contraction of the orbicularis oculi muscles around the eyes, in addition to the zygomaticus major muscles. Fake smiles typically only involve the zygomaticus major muscles, lacking the characteristic eye crinkling.
Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
In conclusion, the zygomaticus major muscles are essential players in facial expression, particularly in the creation of a genuine smile. Understanding their anatomy, function, and the factors that influence their activity is crucial for various fields, including cosmetic surgery, neurology, psychology, and even animation. We hope this comprehensive guide has provided you with a deeper understanding of these vital facial muscles.
As we’ve explored, interventions like Botox can subtly influence these muscles, but it’s paramount to approach such procedures with expertise and a deep understanding of facial anatomy. Understanding these nuances is paramount to achieving optimal results and maintaining a natural expression.
Now that you have a comprehensive understanding of the zygomaticus major muscles, share your experiences with facial expressions or smile enhancement techniques in the comments below. For personalized advice or to explore treatment options, contact our experts for a consultation on facial aesthetics.
