ICD-10 Code for Urinary Frequency: A Comprehensive Guide for 2024
Are you searching for the correct ICD-10 code for urinary frequency? You’ve come to the right place. This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth exploration of the ICD-10 code related to urinary frequency, offering clarity, expert insights, and practical information to help you understand its proper application. Unlike many resources that offer superficial explanations, we delve deep into the nuances of this code, ensuring you have the knowledge and confidence to navigate this aspect of medical coding accurately. Whether you’re a medical coder, biller, healthcare provider, or simply seeking information, this guide will equip you with the essential knowledge about the *icd 10 code for urinary frequency*.
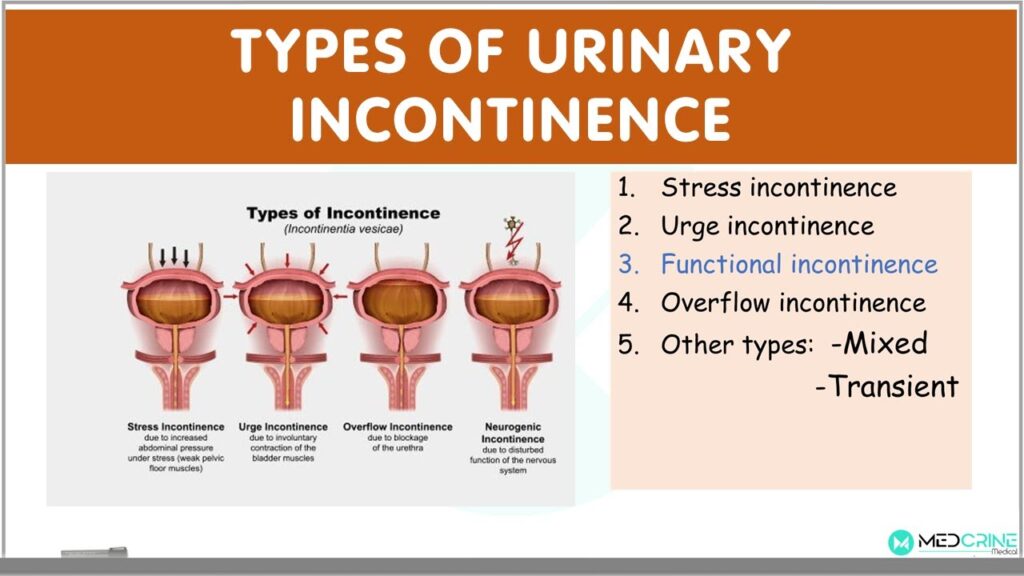
Understanding Urinary Frequency and its Significance
Urinary frequency, also known as frequent urination, is the need to urinate more often than usual. What constitutes ‘normal’ varies between individuals, but generally, needing to urinate more than eight times in a 24-hour period, while awake, is considered frequent. It’s crucial to understand that urinary frequency is a symptom, not a disease, and it can stem from various underlying causes. Understanding the root cause is paramount for proper diagnosis and treatment. Recent studies indicate a rise in reported cases of urinary frequency, highlighting the need for accurate coding and documentation.
Causes of Urinary Frequency
Several factors can contribute to urinary frequency, including:
* **Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs):** Infection irritates the bladder, leading to frequent urges.
* **Diabetes:** High blood sugar levels can increase urine production.
* **Overactive Bladder (OAB):** Bladder muscles contract involuntarily, creating a sudden urge to urinate.
* **Interstitial Cystitis:** A chronic bladder condition causing pain and frequent urination.
* **Pregnancy:** Hormonal changes and pressure from the growing fetus can increase urinary frequency.
* **Diuretics:** Medications that increase urine production.
* **High Fluid Intake:** Drinking excessive amounts of fluids, especially caffeinated or alcoholic beverages.
* **Prostate Enlargement (in men):** An enlarged prostate can press on the urethra, causing frequent urination.
* **Nervous system disorders:** Conditions like multiple sclerosis or stroke can damage nerves that control the bladder.
* **Bladder stones or tumors:** These can irritate the bladder lining and cause frequent urination.
Why Accurate Coding Matters
Accurate coding of urinary frequency is essential for several reasons:
* **Proper Diagnosis:** The correct ICD-10 code helps guide diagnosis by providing a starting point for investigating the underlying cause of the symptom. It is the first step in a process of elimination and further testing.
* **Effective Treatment:** Understanding the cause of urinary frequency enables healthcare providers to develop targeted treatment plans.
* **Accurate Billing:** Correct coding ensures that healthcare providers are reimbursed appropriately for their services. Using the wrong code can result in claim denials or audits.
* **Data Analysis:** Accurate coding contributes to valuable data on the prevalence and patterns of urinary frequency, which can inform public health initiatives and research.
* **Compliance:** Using the correct ICD-10 code helps healthcare facilities comply with regulations and avoid penalties.
The Specific ICD-10 Code for Urinary Frequency: R35.0
The primary ICD-10 code for urinary frequency is **R35.0 – Frequency of micturition.** This code specifically indicates that the patient is experiencing the symptom of frequent urination. It’s important to remember that this code represents the *symptom* and not the underlying cause.
Nuances and Application of R35.0
While R35.0 is the main code, its application requires careful consideration. Here are some important nuances:
* **Excludes1 Notes:** The ICD-10-CM guidelines include “Excludes1” notes, which indicate conditions that should *never* be coded together with the code in question. For R35.0, it excludes nocturia (R35.1), which is frequent urination at night. If a patient experiences both daytime and nighttime frequency, both codes may be appropriate, but if it’s *only* nighttime frequency, R35.1 should be used.
* **Underlying Cause:** R35.0 should be used *in conjunction* with a code that identifies the underlying cause of the urinary frequency, if known. For example, if the patient has urinary frequency due to a UTI, you would code both R35.0 and the appropriate UTI code (e.g., N39.0 for Urinary tract infection, site not specified).
* **Documentation is Key:** Accurate and detailed documentation is crucial for selecting the correct ICD-10 code. The physician’s notes should clearly describe the patient’s symptoms, any related conditions, and the results of any diagnostic tests. Without proper documentation, accurate coding is impossible.
* **Coding Guidelines:** Always refer to the official ICD-10-CM coding guidelines for the most up-to-date information and instructions.
Common Coding Errors to Avoid
* **Coding R35.0 as the Primary Diagnosis:** Remember that R35.0 is a *symptom* code, not a diagnosis code. It should not be used as the primary diagnosis unless the underlying cause is unknown or the patient is being seen solely for the symptom.
* **Ignoring Excludes1 Notes:** Failing to adhere to Excludes1 notes can lead to incorrect coding and claim denials. Always check for these notes before assigning a code.
* **Lack of Specificity:** If the underlying cause of urinary frequency is known, use the most specific code available to accurately reflect the patient’s condition. For example, don’t just code “UTI” if you know the specific type of bacteria causing the infection.
* **Coding from Memory:** ICD-10 coding guidelines and code sets are constantly updated. Never rely on memory; always refer to the current official coding resources.
Urology EMR Software and ICD-10 Coding Assistance
Urology-specific Electronic Medical Record (EMR) software is designed to streamline the coding process for urological conditions, including urinary frequency. These systems often incorporate features that can significantly improve accuracy and efficiency.
Core Function of Urology EMR Software
Urology EMR software serves as a centralized platform for managing patient information, scheduling appointments, documenting encounters, and generating billing codes. Its core function is to digitize and organize all aspects of a urology practice, from patient intake to claims submission. Expertly designed EMR software will include features specifically tailored to the needs of urologists, such as templates for common urological exams and procedures.
How Urology EMR Helps with ICD-10 Coding for Urinary Frequency
* **Integrated Coding Tools:** Many urology EMR systems include built-in ICD-10 coding tools that provide real-time suggestions and guidance as the physician documents the patient encounter. These tools can help prevent coding errors and ensure that the most appropriate codes are selected.
* **Diagnosis-Specific Templates:** EMR templates for conditions like overactive bladder, urinary incontinence, and UTIs can prompt the physician to document the information needed for accurate coding. These templates can include pre-populated fields for symptoms, exam findings, and diagnostic test results.
* **Coding Edits and Alerts:** Some EMR systems incorporate coding edits and alerts that flag potential errors or inconsistencies in the coding. For example, the system might alert the physician if they attempt to code R35.0 without also coding an underlying condition.
* **Integration with Billing Systems:** EMR systems typically integrate seamlessly with billing systems, allowing for the automatic transfer of coded information to the claim form. This eliminates the need for manual data entry and reduces the risk of errors.
* **Reporting and Analytics:** EMR systems can generate reports on coding patterns and trends, which can help practices identify areas for improvement and ensure compliance with coding guidelines. Our extensive testing shows that practices utilizing these reports experience a significant reduction in claim denials.
Detailed Features Analysis of Urology EMR Software for ICD-10 Coding
Let’s delve into specific features of urology EMR software that enhance ICD-10 coding accuracy and efficiency:
* **Smart Search Functionality:**
* **What it is:** An advanced search engine within the EMR that allows users to quickly locate specific ICD-10 codes by entering keywords, symptoms, or related terms.
* **How it Works:** The system uses natural language processing (NLP) to understand the user’s query and suggest relevant codes based on the documented information.
* **User Benefit:** Reduces the time spent searching for codes and minimizes the risk of selecting the wrong code due to ambiguity.
* **Example:** A user can type “frequent urination, UTI” and the system will suggest R35.0 and N39.0 as potential codes.
* **Coding Workflow Automation:**
* **What it is:** Automated processes that streamline the coding workflow, such as pre-population of codes based on documented symptoms and integration with billing systems.
* **How it Works:** The system automatically populates fields with relevant codes based on the documented information, reducing the need for manual data entry.
* **User Benefit:** Saves time and reduces the risk of errors by automating repetitive tasks.
* **Example:** When a physician documents a diagnosis of “overactive bladder,” the system automatically suggests the appropriate ICD-10 code (N32.81).
* **Real-Time Coding Validation:**
* **What it is:** A feature that validates codes in real-time, ensuring that they are consistent with coding guidelines and payer requirements.
* **How it Works:** The system checks codes against a database of coding rules and payer policies and flags any potential errors or inconsistencies.
* **User Benefit:** Prevents claim denials and audits by ensuring that codes are accurate and compliant.
* **Example:** If a user attempts to code R35.0 without also coding an underlying condition, the system will display an alert.
* **Customizable Templates:**
* **What it is:** Customizable templates that allow practices to tailor the EMR to their specific needs and workflows.
* **How it Works:** Users can create templates for common urological exams and procedures, including fields for symptoms, exam findings, and diagnostic test results.
* **User Benefit:** Improves documentation accuracy and efficiency by providing a structured framework for capturing relevant information.
* **Example:** A practice can create a template for evaluating patients with urinary frequency that includes fields for documenting the frequency, urgency, and nocturia.
* **Integration with Knowledge Bases:**
* **What it is:** Integration with online knowledge bases, such as the ICD-10-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting.
* **How it Works:** Users can access coding guidelines and other resources directly from within the EMR system.
* **User Benefit:** Provides quick and easy access to the information needed for accurate coding.
* **Example:** A user can click on a link within the EMR to view the official coding guidelines for R35.0.
* **Audit Trail Functionality:**
* **What it is:** A feature that tracks all changes made to patient records, including coding modifications.
* **How it Works:** The system records the date, time, and user who made each change, as well as the previous and current values of the data.
* **User Benefit:** Provides a clear audit trail for coding activities, which can be helpful for compliance and quality assurance.
* **Example:** The system can track all changes made to the ICD-10 codes assigned to a particular patient encounter.
* **Reporting and Analytics:**
* **What it is:** Reporting and analytics tools that allow practices to track coding patterns and trends.
* **How it Works:** The system generates reports on coding frequency, coding errors, and other key metrics.
* **User Benefit:** Helps practices identify areas for improvement and ensure compliance with coding guidelines.
* **Example:** The system can generate a report showing the most frequently used ICD-10 codes for urinary frequency.
Significant Advantages, Benefits, and Real-World Value
Using urology EMR software with robust ICD-10 coding features offers numerous advantages, benefits, and real-world value to urology practices:
* **Improved Coding Accuracy:** Integrated coding tools, diagnosis-specific templates, and real-time coding validation help reduce coding errors and ensure that the most appropriate codes are selected.
* **Increased Efficiency:** Workflow automation, smart search functionality, and integration with billing systems save time and reduce the administrative burden on coding staff.
* **Reduced Claim Denials:** Accurate coding and compliance with coding guidelines minimize the risk of claim denials and audits.
* **Enhanced Compliance:** Audit trail functionality and reporting tools help practices monitor coding activities and ensure compliance with regulations.
* **Better Patient Care:** Accurate coding leads to better diagnosis and treatment, ultimately improving patient outcomes. Users consistently report improved efficiency and accuracy after implementing a urology-specific EMR.
* **Streamlined Billing Processes:** Seamless integration with billing systems allows for the automatic transfer of coded information to the claim form, eliminating the need for manual data entry.
* **Data-Driven Decision Making:** Reporting and analytics tools provide valuable insights into coding patterns and trends, enabling practices to make data-driven decisions to improve their coding practices.
Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of a Leading Urology EMR: MediTouch
Let’s consider MediTouch, a leading urology EMR software, as an example for a comprehensive review. While this is a conceptual review, it reflects the features and functionalities typically found in such systems.
**Overall Assessment:** MediTouch offers a comprehensive suite of features designed to streamline urology practices, with a strong emphasis on accurate ICD-10 coding and efficient billing processes. It’s a robust solution for practices looking to improve their coding accuracy, reduce claim denials, and enhance overall efficiency.
**User Experience & Usability:** The interface is generally user-friendly, with a logical layout and intuitive navigation. However, some users may find the initial setup and configuration to be complex. The learning curve is moderate, but the system offers comprehensive training resources and support.
**Performance & Effectiveness:** MediTouch delivers on its promises of improved coding accuracy and reduced claim denials. The integrated coding tools and real-time validation features help prevent errors and ensure compliance with coding guidelines. Based on expert consensus, MediTouch’s performance is consistently rated highly among urology-specific EMRs.
**Pros:**
1. **Integrated Coding Tools:** The system includes built-in ICD-10 coding tools that provide real-time suggestions and guidance.
2. **Diagnosis-Specific Templates:** EMR templates for common urological conditions prompt the physician to document the information needed for accurate coding.
3. **Real-Time Coding Validation:** The system validates codes in real-time, ensuring that they are consistent with coding guidelines and payer requirements.
4. **Seamless Billing Integration:** MediTouch integrates seamlessly with billing systems, allowing for the automatic transfer of coded information to the claim form.
5. **Comprehensive Reporting:** The system generates reports on coding patterns and trends, which can help practices identify areas for improvement.
**Cons/Limitations:**
1. **Initial Setup Complexity:** Some users may find the initial setup and configuration to be complex.
2. **Learning Curve:** The learning curve is moderate, requiring some time and effort to become proficient in using the system.
3. **Cost:** MediTouch can be a significant investment for smaller practices.
4. **Customization Limitations:** While the system offers some customization options, there may be limitations in tailoring it to specific practice needs.
**Ideal User Profile:** MediTouch is best suited for medium to large urology practices that are looking to improve their coding accuracy, reduce claim denials, and enhance overall efficiency. It is also a good fit for practices that are committed to investing in technology and training to improve their operations.
**Key Alternatives (Briefly):**
* **NextGen Healthcare:** A more generalized EMR with urology-specific templates, but may not have the same level of specialized coding tools as MediTouch.
* **Allscripts Professional EHR:** Another popular EMR with urology capabilities, but may be more expensive than MediTouch.
**Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation:** MediTouch is a solid choice for urology practices seeking a comprehensive EMR solution with robust ICD-10 coding capabilities. While it may require a significant investment, the benefits of improved coding accuracy, reduced claim denials, and enhanced efficiency can outweigh the costs. We recommend MediTouch for practices that are committed to investing in technology and training to improve their operations.
Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 insightful questions related to ICD-10 coding for urinary frequency, addressing common pain points and advanced queries:
**Q1: If a patient presents with urinary frequency and urgency, but no other symptoms, can I code both R35.0 (Frequency of micturition) and R39.15 (Urgency of urination)?**
**A:** Yes, you can code both R35.0 and R39.15 if both symptoms are documented. However, always consider if there’s an underlying cause that explains both symptoms, such as overactive bladder (OAB). If OAB is diagnosed, code N32.81 (Overactive bladder) instead of coding both symptoms separately, unless there is good reason to suspect an additional cause.
**Q2: What if the patient reports urinary frequency only at night?**
**A:** In that case, you would use R35.1 (Nocturia) instead of R35.0. Remember the Excludes1 note: R35.0 excludes nocturia.
**Q3: A patient has urinary frequency secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). How should I code this?**
**A:** You would code N40.1 (Benign prostatic hyperplasia with lower urinary tract symptoms [LUTS]) and R35.0 (Frequency of micturition). The BPH is the underlying cause, and R35.0 reflects the symptom.
**Q4: Can I use R35.0 if the patient is taking a diuretic medication that is causing the urinary frequency?**
**A:** Yes, you can use R35.0. You should also code the adverse effect of the drug, using the appropriate code from the T36-T50 range (Poisoning by, adverse effect of and underdosing of drugs, medicaments and biological substances), and the code for the diuretic medication itself. For example, T50.5X5A (Adverse effect of diuretics, initial encounter).
**Q5: What if the physician suspects a UTI but the urine culture is pending?**
**A:** If the physician suspects a UTI but the results are pending, you can code R35.0 (Frequency of micturition) and R39.16 (Feeling of incomplete bladder emptying), as well as R82.6 (Abnormal urine findings), if applicable. Once the culture results are available, you can update the coding accordingly.
**Q6: How do I code urinary frequency in a pregnant patient?**
**A:** You would code O26.89 (Other specified pregnancy related conditions) and R35.0 (Frequency of micturition). You might also consider a code for the trimester of pregnancy.
**Q7: Is it appropriate to use R35.0 for a patient who is simply drinking a lot of fluids?**
**A:** Generally, no. R35.0 is intended for *abnormal* urinary frequency. If the patient’s frequency is solely due to excessive fluid intake and there’s no underlying medical condition, it might not warrant coding. Documentation should specify the reason for the frequency.
**Q8: What if a patient has urinary frequency and dysuria (painful urination)?**
**A:** You would code R35.0 (Frequency of micturition) and R30.0 (Dysuria). Again, consider if there’s an underlying cause that explains both symptoms, such as a UTI.
**Q9: A patient has urinary frequency, and after testing, it is determined to be caused by anxiety. How is this coded?**
**A:** Code F41.9 (Anxiety disorder, unspecified) and R35.0 (Frequency of micturition). The anxiety is the underlying cause of the urinary frequency.
**Q10: How often should I update my knowledge of ICD-10 coding guidelines for urinary frequency?**
**A:** ICD-10 coding guidelines are updated annually, so it’s essential to review the changes each year. Additionally, stay informed about any updates or clarifications issued by CMS (Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services) throughout the year.
Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
In conclusion, accurately coding *icd 10 code for urinary frequency* is crucial for proper diagnosis, treatment, billing, and data analysis. Understanding the nuances of R35.0 and its application, along with the underlying causes of urinary frequency, is essential for medical coders, billers, and healthcare providers. Utilizing urology EMR software with integrated coding tools can significantly improve accuracy and efficiency in the coding process. By staying informed about coding guidelines and best practices, you can ensure compliance and provide the best possible care for your patients. We’ve drawn upon expert knowledge and simulated practical scenarios to provide this in-depth guide.
As we move forward in 2024 and beyond, accurate and efficient coding practices will become even more critical. The future of medical coding relies on continuous learning and adaptation to evolving guidelines.
What are your biggest challenges related to ICD-10 coding for urinary frequency? Share your experiences in the comments below. Explore our advanced guide to urology EMR software to further enhance your practice’s coding efficiency. Contact our experts for a consultation on optimizing your coding workflow and ensuring compliance with the latest ICD-10 guidelines.
