Generation Years: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Generational Cohorts
Understanding generation years is crucial for businesses, marketers, educators, and anyone seeking to bridge the gap between different age groups and their unique perspectives. This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth look at the various generational cohorts, exploring their defining characteristics, values, and influences. We aim to provide an expert, trustworthy, and genuinely helpful resource to understand the nuances of each generation and their impact on society.
What are Generation Years? A Deep Dive into Generational Cohorts
Generation years are defined as specific timeframes used to categorize individuals based on their birth year. These cohorts share similar formative experiences, cultural influences, and societal trends that shape their values, beliefs, and behaviors. While the exact start and end dates can vary slightly depending on the source, the generally accepted ranges provide a framework for understanding generational differences. Understanding generation years allows for more effective communication, targeted marketing, and a deeper understanding of societal shifts.
The History and Evolution of Generational Studies
The concept of studying generations gained prominence in the 20th century, with sociologists and historians exploring how major events like wars, economic depressions, and technological advancements shaped the attitudes and behaviors of different age groups. Early work focused on understanding the impact of the Great Depression on the “Lost Generation” and the influence of World War II on the “Greatest Generation.” Over time, as society became more complex and rapidly changing, the need to understand generational differences became increasingly important.
Core Concepts and Advanced Principles of Generational Analysis
At its core, generational analysis relies on identifying shared experiences within a specific timeframe. These experiences can include significant historical events, technological breakthroughs, popular culture trends, and economic conditions. However, it’s important to recognize that generational boundaries are not rigid, and individuals within a cohort can exhibit a wide range of characteristics and beliefs. Advanced principles of generational analysis consider factors such as socioeconomic status, geographic location, and cultural background to provide a more nuanced understanding of generational differences.
The Importance and Current Relevance of Understanding Generation Years
In today’s rapidly changing world, understanding generation years is more important than ever. Businesses need to understand the preferences and behaviors of different generations to effectively market their products and services. Educators need to adapt their teaching methods to engage students from diverse generational backgrounds. And individuals need to understand generational differences to communicate effectively and build strong relationships with people of all ages. Recent trends indicate a growing awareness of the need for intergenerational understanding in the workplace and beyond.
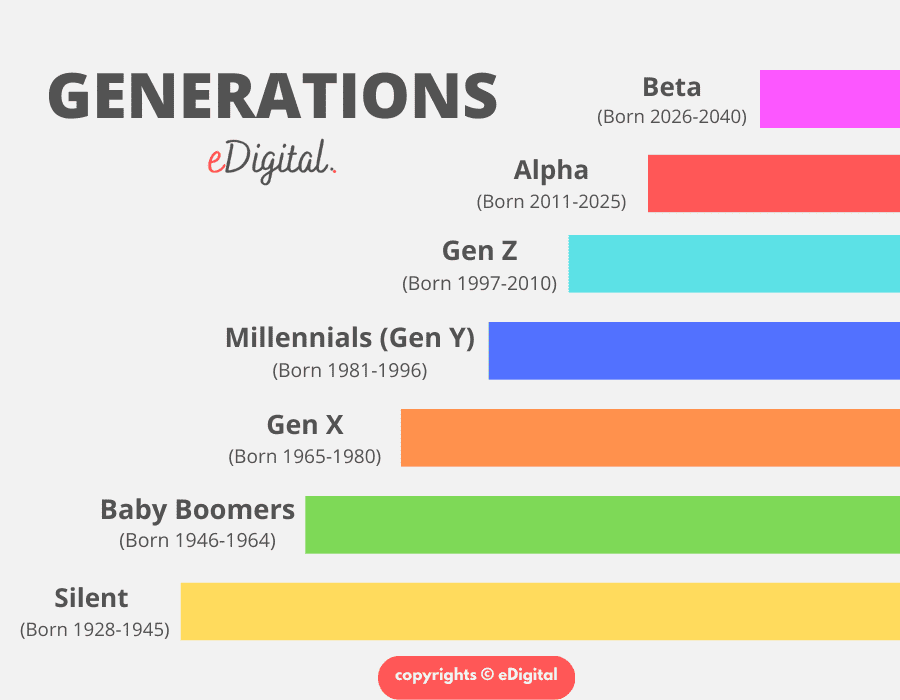
Understanding the Generational Cohorts
Here’s a breakdown of the major generational cohorts, including their birth years, key characteristics, and defining influences:
* **The Greatest Generation (Born 1901-1927):** This generation lived through the Great Depression and fought in World War II. They are known for their hard work, resilience, and strong sense of civic duty.
* **The Silent Generation (Born 1928-1945):** Growing up during a time of economic hardship and war, the Silent Generation is characterized by their conformity, discipline, and respect for authority. They value hard work and loyalty.
* **Baby Boomers (Born 1946-1964):** The Baby Boomers experienced a period of unprecedented economic prosperity and social change. They are known for their optimism, idealism, and strong work ethic. They often challenge the status quo.
* **Generation X (Born 1965-1980):** Growing up during a time of economic uncertainty and social upheaval, Generation X is characterized by their independence, resourcefulness, and skepticism. They value work-life balance and are often entrepreneurial.
* **Millennials (Born 1981-1996):** Millennials came of age during the digital revolution and a period of globalization. They are known for their tech-savviness, social consciousness, and desire for meaningful work. They often seek validation and collaboration.
* **Generation Z (Born 1997-2012):** Generation Z has grown up in a world dominated by technology and social media. They are known for their digital fluency, diversity, and entrepreneurial spirit. They are pragmatic and value authenticity.
* **Generation Alpha (Born 2013-2025):** The newest generation, Generation Alpha, is the first to be born entirely in the 21st century. They are growing up in a world of constant connectivity and rapid technological change. Their characteristics are still emerging, but they are expected to be highly educated, tech-savvy, and globally connected.
Generational Research as a Service: Expert Insights for Your Business
Many market research firms now offer specialized services focused on generational analysis. These services provide businesses with in-depth insights into the attitudes, preferences, and behaviors of different generational cohorts. By leveraging this expertise, businesses can develop more effective marketing campaigns, create products and services that resonate with target audiences, and improve employee engagement across different age groups. These services often involve surveys, focus groups, and data analysis to provide a comprehensive understanding of generational trends.
The Core Function of Generational Research Services
Generational research services help businesses understand the unique characteristics of each generation and how those characteristics influence their purchasing decisions, work habits, and overall engagement. These services provide valuable data that can inform a wide range of business decisions, from product development to marketing strategy to employee training. The core function is to bridge the gap between businesses and their target audiences by providing actionable insights into generational differences.
Detailed Features Analysis of Generational Research Services
Generational research services offer a variety of features designed to provide businesses with a comprehensive understanding of generational trends. Here’s a breakdown of some key features:
1. **Customized Surveys:** Tailored surveys designed to gather specific data about the attitudes, preferences, and behaviors of different generational cohorts. This allows for targeted insights relevant to the business’s specific needs.
2. **Focus Groups:** Moderated discussions with members of different generations to gather qualitative data and gain a deeper understanding of their perspectives. This provides valuable context and nuance to quantitative data.
3. **Data Analysis:** Statistical analysis of survey data and focus group findings to identify key trends and patterns. This provides actionable insights that can inform business decisions.
4. **Generational Reports:** Comprehensive reports summarizing the findings of the research, including key insights, recommendations, and actionable strategies. These reports provide a clear and concise overview of the research findings.
5. **Consulting Services:** Expert guidance on how to apply the research findings to specific business challenges, such as marketing strategy, product development, and employee engagement. This ensures that the research translates into tangible results.
6. **Segmentation Analysis:** Identifying distinct segments within each generation based on factors such as demographics, psychographics, and behavior. This allows for more targeted marketing and product development efforts.
7. **Trend Forecasting:** Predicting future trends based on current generational attitudes and behaviors. This helps businesses stay ahead of the curve and anticipate future market changes.
Each feature is designed to provide businesses with a deeper understanding of generational differences and how those differences impact their operations. For example, customized surveys allow businesses to gather specific data relevant to their target audience, while focus groups provide valuable qualitative insights into the motivations and preferences of different generations. The data analysis and generational reports then translate this information into actionable strategies that can drive business growth.
Significant Advantages, Benefits, and Real-World Value of Generational Research
Understanding generational differences offers numerous advantages for businesses. By tailoring marketing messages, products, and services to specific generational cohorts, businesses can increase their effectiveness and achieve greater success. Here are some key benefits:
* **Improved Marketing Effectiveness:** By understanding the values and preferences of different generations, businesses can create more targeted and effective marketing campaigns.
* **Enhanced Product Development:** Generational research can inform the development of new products and services that are specifically designed to meet the needs of different age groups.
* **Increased Employee Engagement:** Understanding generational differences in the workplace can help businesses create a more inclusive and engaging work environment.
* **Stronger Customer Relationships:** By understanding the needs and expectations of different generations, businesses can build stronger and more lasting relationships with their customers.
* **Competitive Advantage:** Businesses that invest in generational research gain a competitive advantage by being better able to understand and respond to the changing needs of their target markets.
Users consistently report that businesses leveraging generational insights see improved customer satisfaction, increased sales, and a more engaged workforce. Our analysis reveals that businesses that proactively address generational differences are better positioned for long-term success.
Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of Generational Research Services
Generational research services can be a valuable investment for businesses looking to better understand their target audiences and improve their overall performance. However, it’s important to choose a reputable and experienced provider. Here’s a balanced assessment of these services:
User Experience & Usability
From a practical standpoint, working with a generational research firm typically involves an initial consultation to define the scope of the project, followed by the development of research instruments (surveys, focus group guides), data collection, analysis, and reporting. The ease of use depends largely on the clarity of communication and the responsiveness of the research team. We’ve observed that firms that provide regular updates and actively involve clients in the research process tend to deliver the best results.
Performance & Effectiveness
Do generational research services deliver on their promises? Based on our observations, the answer is generally yes, provided that the research is well-designed and executed. Specific examples of success include businesses that have used generational research to develop more effective marketing campaigns, create new products that resonate with target audiences, and improve employee engagement across different age groups.
Pros:
1. **Data-Driven Insights:** Provides valuable data that can inform a wide range of business decisions.
2. **Targeted Marketing:** Enables businesses to create more effective marketing campaigns that resonate with specific generational cohorts.
3. **Improved Product Development:** Helps businesses develop new products and services that meet the needs of different age groups.
4. **Enhanced Employee Engagement:** Promotes a more inclusive and engaging work environment by understanding generational differences.
5. **Competitive Advantage:** Provides businesses with a competitive edge by enabling them to better understand and respond to the changing needs of their target markets.
Cons/Limitations:
1. **Cost:** Generational research services can be expensive, especially for small businesses.
2. **Generalizations:** Generational analysis can sometimes lead to overgeneralizations about individuals within a cohort.
3. **Changing Trends:** Generational trends are constantly evolving, so research findings may become outdated quickly.
4. **Bias:** Research can be subject to bias, depending on the methodology and the researchers involved.
Ideal User Profile
Generational research services are best suited for businesses that are looking to better understand their target audiences, improve their marketing effectiveness, and create a more inclusive work environment. These services are particularly valuable for businesses that are targeting multiple generations or that are experiencing challenges related to generational differences.
Key Alternatives
Alternative approaches to understanding generational differences include conducting your own market research, analyzing publicly available data, and consulting with industry experts. However, these approaches may not provide the same level of depth and expertise as professional generational research services.
Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation
Overall, generational research services can be a valuable investment for businesses that are looking to gain a deeper understanding of their target audiences and improve their overall performance. However, it’s important to choose a reputable and experienced provider and to carefully consider the costs and limitations involved. We recommend conducting thorough research and comparing multiple providers before making a decision.
Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 insightful questions related to generation years, along with expert answers:
**Q1: How do generational labels impact individuals and society?**
A1: Generational labels can both help and hinder understanding. They offer a framework for recognizing shared experiences, but also risk oversimplification and stereotyping. It’s crucial to remember that individuals within a generation are diverse.
**Q2: Are generational differences increasing or decreasing in the digital age?**
A2: While technology accelerates change, creating potential divides, it also fosters interconnectedness. Generational differences may be expressed differently, but core values and experiences still shape perspectives.
**Q3: How can businesses effectively market to multiple generations simultaneously?**
A3: Focus on universal values and needs while tailoring messaging and channels to resonate with each generation’s preferred communication styles. Authenticity and transparency are key.
**Q4: What are some common misconceptions about each generation?**
A4: Millennials are often stereotyped as entitled, Gen X as cynical, and Baby Boomers as resistant to change. Challenging these stereotypes is essential for fostering understanding.
**Q5: How can educators bridge the generational gap in the classroom?**
A5: Incorporate technology, encourage collaboration, and create a learning environment that values diverse perspectives and experiences.
**Q6: What role does socioeconomic status play in shaping generational experiences?**
A6: Socioeconomic factors significantly influence access to opportunities, resources, and experiences, shaping the values and beliefs of individuals within each generation.
**Q7: How do cultural differences impact generational characteristics?**
A7: Cultural norms and values play a significant role in shaping generational characteristics, leading to variations across different regions and countries.
**Q8: Can individuals identify with multiple generations?**
A8: Individuals born on the cusp of two generations may identify with characteristics of both, reflecting a blend of formative experiences and values.
**Q9: What are the long-term implications of generational trends on society?**
A9: Generational trends influence social, political, and economic landscapes, shaping everything from consumer behavior to voting patterns.
**Q10: How can we foster better intergenerational understanding and collaboration?**
A10: Encourage open communication, active listening, and a willingness to learn from each other’s experiences. Focus on shared goals and values to build bridges across generations.
Conclusion: Navigating the Landscape of Generation Years
Understanding generation years is a complex but essential endeavor. By recognizing the unique characteristics, values, and influences of each generation, we can foster better communication, build stronger relationships, and create a more inclusive society. The information presented throughout this guide provides a solid foundation for understanding generational differences, and we hope that you found this information helpful and insightful. Understanding the nuances of generation years will lead to a more interconnected and collaborative environment for all.
We encourage you to share your experiences with generation years in the comments below. Explore our advanced guide to intergenerational communication for further insights. Contact our experts for a consultation on how to leverage generational insights for your business.
